XEZ angular contact ball Bearing matching mode, code introduction, XEZ ball bearings and other brands of bearing model comparison.
XEZ BEARING TYPE IDENTIFICATION

| H | Structure notation | No mark: ordinary high speed; B: Improved high speed; H: Super high speed series |
| 7 | Bearing form mark | 7: Single row angular contact ball bearing |
| 0 | Dimensional Series Code | Thou hast series; All series; 0: 10 series; 2: 02 series |
| 02 | Internal code | 03 below bearing inner diameter: 00:10mm; 01:12 mm; 02:15 mm; 03 : 17mm 04 above bearing inner diameter = inner diameter code X5 (mm) |
| C | Contact Angle mark | C: 15° AC: 25° |
| T | Cage mark | T: The outer ring guides the bakelite cage; TN: Roller guide nylon cage; M: Brass cage |
| 2RZ | Seal form mark | Unmarked: Open;2R B non-contact rubber sealing ring 2RS: contact rubber sealing ring |
| HQ1 | Roller material mark | No mark: steel ball (GCR15); HQ1: Ceramic Ball (Sian,); HV: stainless steel ball (9Cr18) |
| P4 | Accuracy of the mark | P2: ISO2; P4: ISO4; P5: ISO5; P4S: Dimensional accuracy ISO4, Rotation accuracy ISO2 |
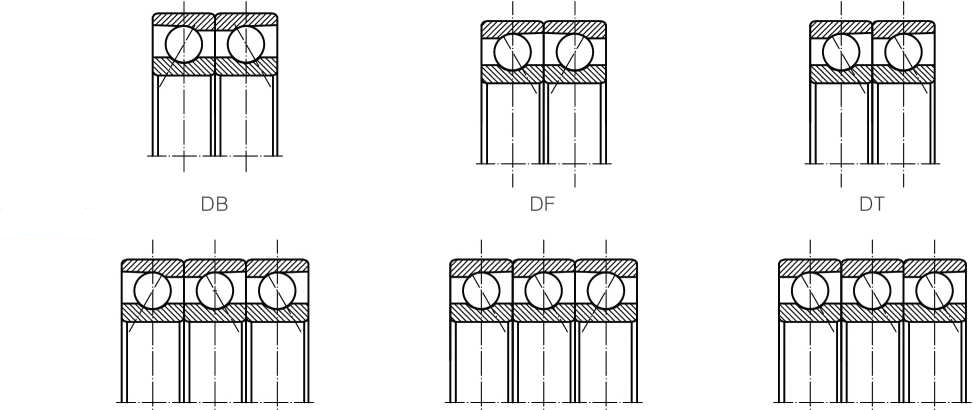
| DB | Combination of mark | G: Single-row universal pairing; DU: double-column universal pairing; DB: Back-to-back pairing; DF: Face-to-face pairing; DT: Parallel pairing |
| A | Preloaded mark | A: light pretightening; B: middle preloading; C: Heavy preloading; Ca: light pre-clearance; CB: middle pre-clearance; CC: Re-pre-clearance |
BEARING TYPE ANTITHESIS
| Project | Type | XEZ code | SKF | NSK | FAG | SNFA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Ultra-light series | 718 | 718 | 78 | B718 | SEA |
| Light series, | 719 | 719 | 79 | B719 | SEB | |
| High speed super light series | H719 | 719CE | BN19 | HS719 | VEB | |
| Light series | 70 | 70 | 70 | B70 | EX | |
| High speed light series | H70 | 70CE | BN10 | HS70 | VEX | |
| Standard series | 72 | 72 | 72 | B72 | E200 | |
| Precision grade | P5 | P5 | P5 | 5 | ||
| P4 | P4A | P4 | P4S | 7 | ||
| P2 | PA9A | P2 | P2 | 9 | ||
| Contact Angle | 15 degrees | C | CD | C | C | 1 |
| 25 degrees | AC | ACD | A5 | E | 3 | |
| Equipping way | < > | DB | DB | DB | DU (0) | DD |
| > < | DF | DF | DF | DU (X) | FF | |
| < < | DT | DT | DT | DU (T) | T | |
| < < > | TBT | TBT | DBD | TD | ||
| > < < | TFT | TFT | DFD | TF | ||
| < > | QBC | QBC | DBB | TDT | ||
| < > | QBT | QBT | QBT | 3DT | ||
| Universal matching | G | G | SU | U | U | |
| Pre-tightening force | light | A | A | L | L | L |
| medium | B | B | M | M | M | |
| heavy | C | C | H | S | F |
SPECIFICATIONS OF MATCHED ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS
The assembled bearings can bear radial and axial combined loads, which are mainly radial loads, and can also bear pure radial loads. The assembled bearings are composed of single row angular contact ball bearings of the same specifications in different assembly modes. The specific assembly modes are as follows:
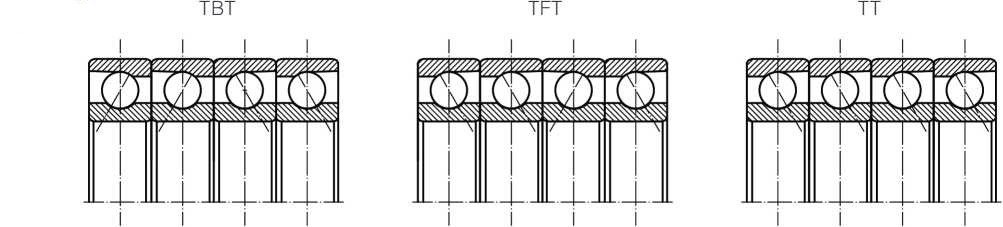
QBC QFC QT
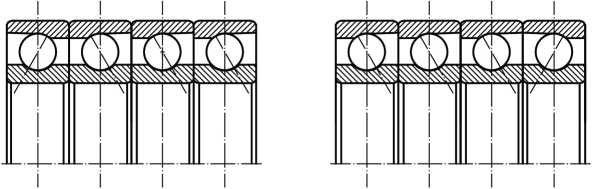
QBT QFT
What is the difference between back-to-back DB (O-Arrangement) and face-to-face DF (X-Arrangement) installation of angular contact ball bearing?
BACK-TO-BACK (O-Arrangement)
Advantages:
1)Less sensitive to the thermal gradient than the face-to-face arrangement
2)Easy mounting on the shaft
3)Self contained assembly on the shaft
Disadvantages :
1)Higher sensitivity to misalignment than face-to-face
2)Difficult dismounting
BACK-TO-BACK (O-Arrangement)
Advantages
Higher misalignment capabilities than back-to-back
Permits disassembly in screw compressors without destroying one of the bearings.
Disadvantages
No self-contained assembly on the shaft
More sensitive to thermal gradient than back-to-back


